Offline replication (air gap)
Introduction
Delphix replication typically transfers data from a source engine to a target engine over a TCP network, with the source communicating directly with the target.
In some cases, compliance or security requirements prohibit direct network connectivity between engines. In these scenarios, offline replication (also called air gap replication) enables data transfer without a network connection.
Offline replication works by writing replication data to an NFS share from the source engine. Later, the target engine reads the data from the NFS share. At no point during this workflow do the two engines communicate directly.
Prerequisites
To use offline replication:
-
Source engines must have an offline replication spec configured with the correct NFS share.
-
Target engines must have an offline receive spec referencing the correct NFS share and the unique tag of the corresponding send spec.
-
NFS shares can be distinct for send and receive engines.
-
Delphix Engines access NFS shares as root, so the root user on each engine must have read/write permissions.
-
Offline replication stages data on the local database storage before transferring it to or from the NFS share, so enough free space must exist to accommodate the maximum size of the objects being replicated.
Limitations
-
NFS mounts only
Currently, only NFS mounts are supported for air gap replication. -
CLI-focused
Most offline replication operations are performed via the Continuous Data CLI. The CD UI can display and update (but not create) offline send specs; offline receive specs are accessible only via CLI/API. -
DCT support
All offline replication CRUD operations are supported via Data Control Tower (DCT). -
Data Vault locking
Offline receive specs cannot currently be locked as a Data Vault. -
SDD support
Selective Data Distribution (SDD) is not currently supported with offline replication.
1-to-many and serialization points
Offline replication writes each initial or incremental update as a serialization point on the NFS share. The share is the only transfer path, so retention and ordering are critical.
1-to-many topology
-
A single offline send spec can feed multiple targets.
-
Each target creates its own receive spec pointing to the same NFS share.
-
As long as all updates remain on the share, every target can receive an identical data set by applying updates through the same serialization point.
Retention rules
-
The NFS share owner is responsible for cleanup.
-
If a required serialization point is deleted before a target receives it, the receive cannot be recovered or “fixed.”
-
Use getLastReceivedInfo to identify which directories are safe to remove.
Receive ordering
-
A receive job applies only the next single serialization point, even if newer ones exist.
-
If the source sends multiple times before the target receives, the target must run one receive per pending point to catch up.
GUI, API, or CLI changes
Offline replication is currently API/CLI-centric, with full UI support planned exclusively for DCT.
The CD UI lists offline send specs similarly to regular replication specs:
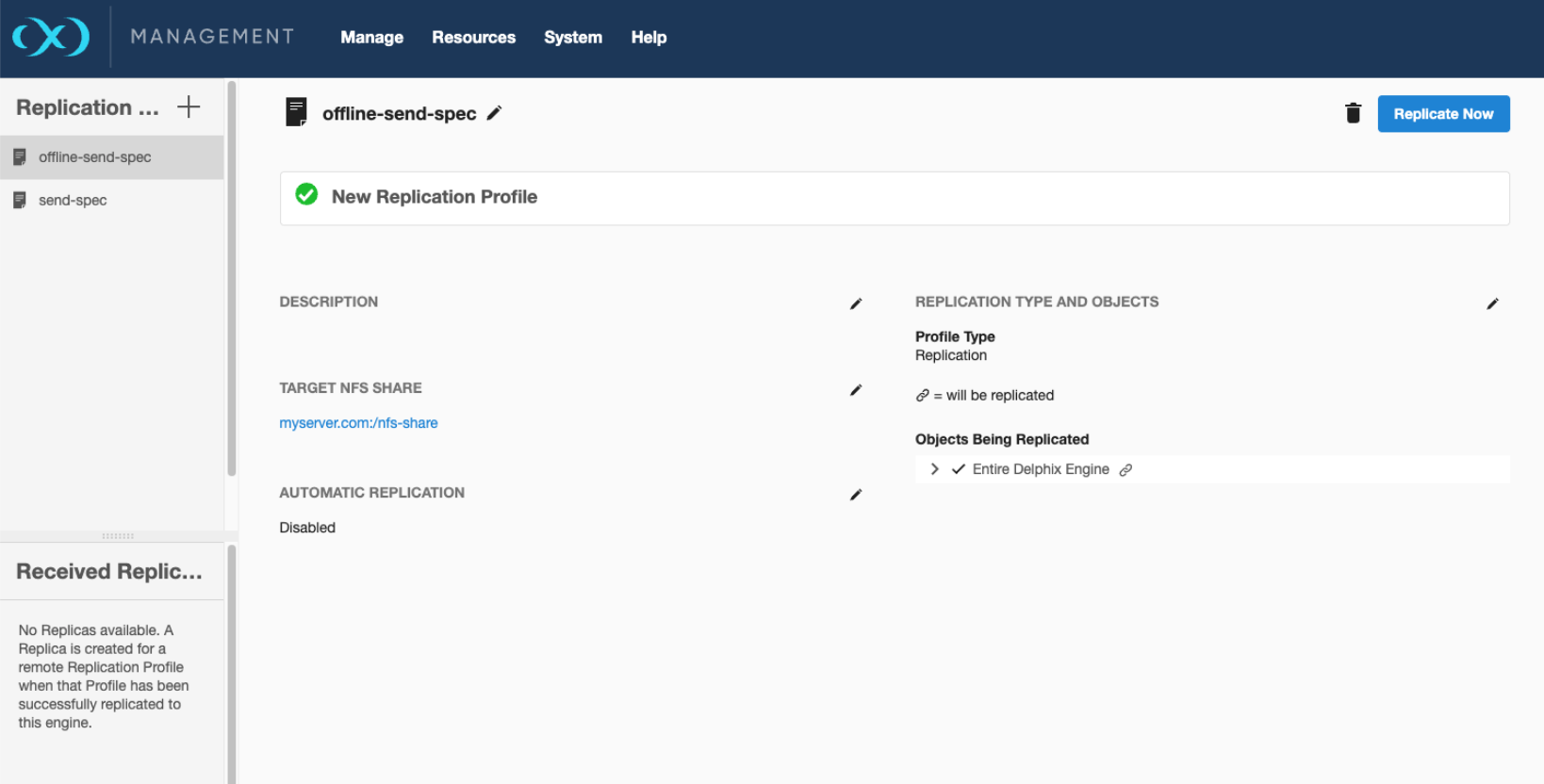
Network vs. offline DataTraffic
Offline and network replication specs share a common DataTraffic class. Properties specific to network or offline specs appear only when relevant.
Network replication spec example (CLI):
ip-10-110-245-194 replication spec 'send-spec'> ls
Properties
type: ReplicationSpec
name: send-spec
automaticReplication: false
dataTraffic:
type: ReplicationNetworkTraffic
bandwidthLimit: 0
encrypted: false
numberOfConnections: 1
targetCredential:
type: PasswordCredential
password: ********
targetHost: myhost.com
targetPort: 0
targetPrincipal: admin
useSystemSocksSetting: false
description: (unset)
lockedProfile: false
objectSpecification:
type: ReplicationList
name: (unset)
objects: domain0
reference: REPLICATION_SPEC-1
runtime:
type: ReplicationSpecRuntime
schedule: (unset)
tag: f631d6f1-c62b-45c1-ba0c-385354d3410bOffline send spec example (CLI):
ip-10-110-221-50 replication spec 'offline-send-spec'> ls
Properties
type: ReplicationSpec
name: offline-send-spec
automaticReplication: false
dataTraffic:
type: ReplicationOfflineTraffic
nfsShare: myserver.com:/nfs-share
description: (unset)
lockedProfile: false
objectSpecification:
type: ReplicationList
name: (unset)
objects: domain0
reference: REPLICATION_SPEC-2
runtime:
type: ReplicationSpecRuntime
schedule: (unset)
tag: b18c4ade-75fe-44f4-afde-f244366a2edbCRUD operations for offline specs
Send specs use the same APIs as network send specs. Ensure dataTraffic.type=ReplicationOfflineTraffic.
Receive specs use the new /delphix/replication/receive endpoint for all CRUD operations.
Creating an offline send spec (CLI):
ip-10-110-245-194 replication spec create *> set dataTraffic.type=ReplicationOfflineTraffic
ip-10-110-245-194 replication spec create *> set name=offline-send-spec
ip-10-110-245-194 replication spec create *> set dataTraffic.nfsShare=myserver.com:/nfs-share
ip-10-110-245-194 replication spec create *> set objectSpecification.objects=domain0
ip-10-110-245-194 replication spec create *> commit
`REPLICATION_SPEC-2
ip-10-110-245-194>Offline receive spec example (CLI):
ip-10-110-224-220 replication receive 'rcv-spec'> ls
Properties
type: OfflineReplicationReceiveSpec
name: rcv-spec
automaticReplication: false
description: (unset)
nfsShare: myserver.com:/nfs-share
reference: OFFLINE_REPLICATION_RECEIVE_SPEC-1
schedule: (unset)
tag: f631d6f1-c62b-45c1-ba0c-385354d3410bCreating an offline receive spec (CLI):
ip-10-110-245-194 replication receive> create
ip-10-110-245-194 replication receive create *> set name=offline-receive-spec
ip-10-110-245-194 replication receive create *> set nfsShare=myserver.com:/nfs-share
ip-10-110-245-194 replication receive create *> set tag=b18c4ade-75fe-44f4-afde-f244366a2edb
ip-10-110-245-194 replication receive create *> commit
`OFFLINE_REPLICATION_RECEIVE_SPEC-2Executing offline replication
Send spec
ip-10-110-221-50 replication spec 'offline-send-spec' execute *> commit
Dispatched job JOB-1996
REPLICATION_SEND job started for "offline-send-spec".
Executing replication spec "offline-send-spec" ("b18c4ade-75fe-44f4-afde-f244366a2edb").
Starting initial replication update.
Preparing replication update.
Sending metadata.
Sending metadata - phase 2.
Sending data for "[Untitled/CDOMLOSRC8EE]".
Sending data for "[Untitled/CDOMLOSRC8EEPDB3-nq-19-src.dlpxdc.co]".
Sending data for "[Untitled/CDOMLOSRC8EEPDB1-nq-19-src.dlpxdc.co]".
Sending data for "[Untitled/CDOMLOSR-S960XX-1752874656988]".
Sending data for "[Untitled/CDOMLOTG0C79]".
Transferring data to NFS share.Receive spec
ip-10-110-224-220 replication receive 'rcv-spec' execute *> commit
Dispatched job JOB-1
REPLICATION_RECEIVE job started for "OfflineSource-1".
Mounting NFS share myserver.com:/nfs-share.
Transferring data from NFS share.
Receiving initial replication update.
Receiving metadata.
Receiving metadata - phase 2.
Applying metadata updates.
Transfer completed in 0:00:00, received 0.00B (0.00B/s).
REPLICATION_RECEIVE job for "OfflineSource-1" completed successfully.Incremental updates work identically by repeating send and receive executions.
Monitoring & cleanup
Offline replication does not remove any data from the NFS share. It is your responsibility to clean up data on the NFS share after a successful receive.
To determine which directories are safe to delete, use the following endpoint: /delphix/replication/receive/{receiveSpecRef}/getLastReceivedInfo
Example
ip-10-110-224-220 replication receive 'rcv-spec'> getLastReceivedInfo
ip-10-110-224-220 replication receive 'rcv-spec' getLastReceivedInfo *> commit
type: OfflineReplicationReceiveInfo
lastOfflineReceiveDataDir: f631d6f1-c62b-45c1-ba0c-385354d3410b/2
lastOfflineSerializationPointId: 2
lastSendTimestamp: 2025-08-15T23:23:25.252ZIn this example:
-
lastOfflineReceiveDataDir=f631d6f1-c62b-45c1-ba0c-385354d3410b/2 -
This identifies the directory on the NFS share that contains the most recently received data.
Directory cleanup rules
-
Directories less than or equal to the last received serialization point (
/1and/2in this example) are safe to delete once the receive job completes. -
Directories greater than the last received serialization point (
/3in this example) must be kept for future receive.
A typical NFS share looks like this:
/nfs-share/
f631d6f1-c62b-45c1-ba0c-385354d3410b/
1/
2/
3/-
/1safe to delete (already received) -
/2safe to delete (last applied) -
/3keep (pending future receive)
Deleting replica namespaces
With offline replication, you must remove the offline replication receive spec before you can delete its replica namespace on the target engine. This is different than network replication, where you can delete a replica namespace directly:
-
Delete the offline receive spec.
Use the CLI to remove the receive spec that owns the replica namespace:Copyip-<target-engine> replication receive 'rcv-spec' delete *> commitReplace
rcv-specwith the name of your offline receive spec.API equivalent:
CopyDELETE /delphix/replication/receive/{receiveSpecRef} -
Delete the replica namespace.
When the receive spec is gone, delete the namespace normally:Copyip-<target-engine> namespace 'ReplicaNamespaceName' delete *> commitReplace
ReplicaNamespaceNamewith your actual namespace name.
If you try to delete the namespace before removing the receive spec, the operation fails because the receive spec owns the namespace.
Common questions
Do the source and target engines ever connect over the network?
No. Offline replication is designed so that neither engine is aware of the other. Both interact only with the specified NFS share. The receive engine requires the tag value from the send spec to locate the correct data, but this is used internally and specified manually during receive spec creation.
How do I know when it’s safe to clean up the air gap server?
Use the getLastReceivedInfo endpoint (shown above) for the relevant offline receive spec.