Fluentd plugin service for API modules
Overview
The Delphix Fluentd plugin service assisted in a feature that provided options for configuring a Delphix engine that forwards events and metrics to a Splunk host. Delphix extended this capability to use with other monitoring packages (ELK Stack, Datadog, etc.). Fluentd plugins provide you a mechanism to customize the Delphix engine’s forwarding capabilities for output to other data consumers.
The Fluentd plugin is a tar file with a configuration template, including any gem files required to execute the directives in the configuration file. When you upload the plugin, the configuration occurs by collecting user input for the variables required by the template. The interfaces change because the set of variables you need is now mutable from plugin to plugin. Splunk configuration is available out of the box with no additional plugins. This feature uses one UI for all Fluentd configurations.
Technical details
Architectural diagram
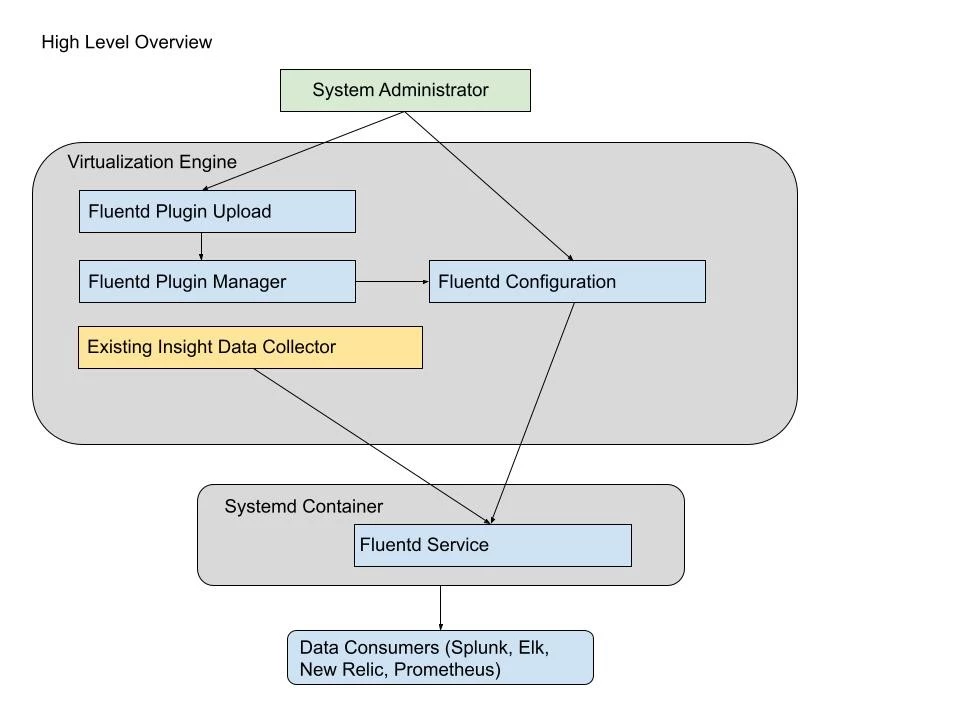
GUI, API or CLI changes (if any)
APIs with a corresponding CLI for uploading plugins and Fluentd configuration have been added. The service/fluentd/plugins API displays the available plugins.
service fluentd plugins> ls
Objects
REFERENCE PLUGIN ATTRIBUTEDEFINITIONS SCHEMADEFINITION
FLUENTD_PLUGIN-1 splunkHec [ ... ] { ... }
Operations
requestUploadTokenThe splunkHec plugin appears by default and cannot be deleted. Additionally, the requestUploadToken operation provides the token you need to upload a plugin via the data/upload API. If you upload a second plugin, it appears in the list. Before you can upload a third plugin, you must select and delete the second plugin.
The following curl commands show how to use the API to upload a plugin:
curl -s -X POST -k --data @- http://<engine-name>/resources/json/delphix/session -c ~/cookies.txt -H "Content-Type: application/json" <<EOF
{
"type": "APISession",
"version": {
"type": "APIVersion",
"major": 1,
"minor": 11,
"micro": 41
}
}
EOF
curl -s -X POST -k --data @- http://<engine-name>/resources/json/delphix/login -b ~/cookies.txt -c ~/cookies2.txt -H "Content-Type: application/json" <<EOF
{
"type": "LoginRequest",
"username": "sysadmin",
"password": "sysadmin",
"target": "SYSTEM"
}
EOF
curl -s -X POST -k --data @- http://<engine-name>/resources/json/delphix/service/fluentd/plugins/requestUploadToken -b ~/cookies2.txt -H "Content-Type: application/json" <<EOF
Returns the token e.g: {"type":"OKResult","status":"OK","result":{"type":"FileUploadResult","url":"/resources/json/delphix/data/upload","token":"59346df5-3ecd-4ced-afbf-97acefa156dc"},"job":null,"action":null}
EOF
curl -b ~/cookies2.txt -X POST -F "file=@/Users/blewis/ws/far-dev/splunk_host_port.far" -F "token=<token>" http:/<engine-name>/resources/json/delphix/data/uploadThe service/fluentd/plugins API displays the available tokens.
An example for creating a configuration with the default splunkHec plugin:
service fluentd configuration> create
service fluentd configuration create *> set plugin=splunkHec; set enabled=true; edit attributes
service fluentd configuration create attributes *> add; set name=hec_host; set value=http://vmname-splunkhost.delphix.com; back
service fluentd configuration create attributes *> add; set name=hec_port; set value=8088; back
service fluentd configuration create attributes *> add; set type=FluentdSecretAttribute;
service fluentd configuration create attributes 2 *> set name=hec_token; set secretValue=bb75c032-bdea-4c19-b152-d158cf13e019; back
service fluentd configuration create attributes *> add; set name=eventsIndex; set value=delphix_events; back
service fluentd configuration create attributes *> add; set name=protocol; set value=https; back
service fluentd configuration create attributes *> add; set name=metricsPushFrequency; set value=60; back
service fluentd configuration create attributes *> add; set name=metricsIndex; set value=delphix_metrics; back
service fluentd configuration create attributes *> add; set name=eventsPushFrequency; set value=60; back
service fluentd configuration create attributes *> add; set name=enable_engine_sys_logs; set value=false; back;
service fluentd configuration create attributes *> add; set name=enable_engine_audit_logs; set value=false; back;
service fluentd configuration create attributes *> ls
Properties
0:
type: FluentdRegularAttribute (*)
name: hec_host (*)
value: http://vmname-splunkhost.delphix.com (*)
1:
type: FluentdRegularAttribute (*)
name: hec_port (*)
value: 8088 (*)
2:
type: FluentdSecretAttribute (*)
name: hec_token (*)
secretValue: ******** (*)
3:
type: FluentdRegularAttribute (*)
name: eventsIndex (*)
value: delphix_events (*)
4:
type: FluentdRegularAttribute (*)
name: protocol (*)
value: https (*)
5:
type: FluentdRegularAttribute (*)
name: metricsPushFrequency (*)
value: 60 (*)
6:
type: FluentdRegularAttribute (*)
name: metricsIndex (*)
value: delphix_metrics (*)
7:
type: FluentdRegularAttribute (*)
name: eventsPushFrequency (*)
value: 60 (*)
8:
type: FluentdRegularAttribute (*)
name: enable_engine_sys_logs (*)
value: false (*)
9:
type: FluentdRegularAttribute (*)
name: enable_engine_audit_logs (*)
value: false (*)
## Use the "add" command to add an element to this array.
service fluentd configuration create attributes *> back
service fluentd configuration create *> ls
Properties
type: FluentdConfig
name: (unset)
attributes: [ ... ] (*)
enabled: true (*)
plugin: splunkHec (*)
service fluentd configuration create *> commitCreating default splunkHec configuration from GUI
-
Log in as a sysadmin user and select Preferences > Fluentd Configuration.
-
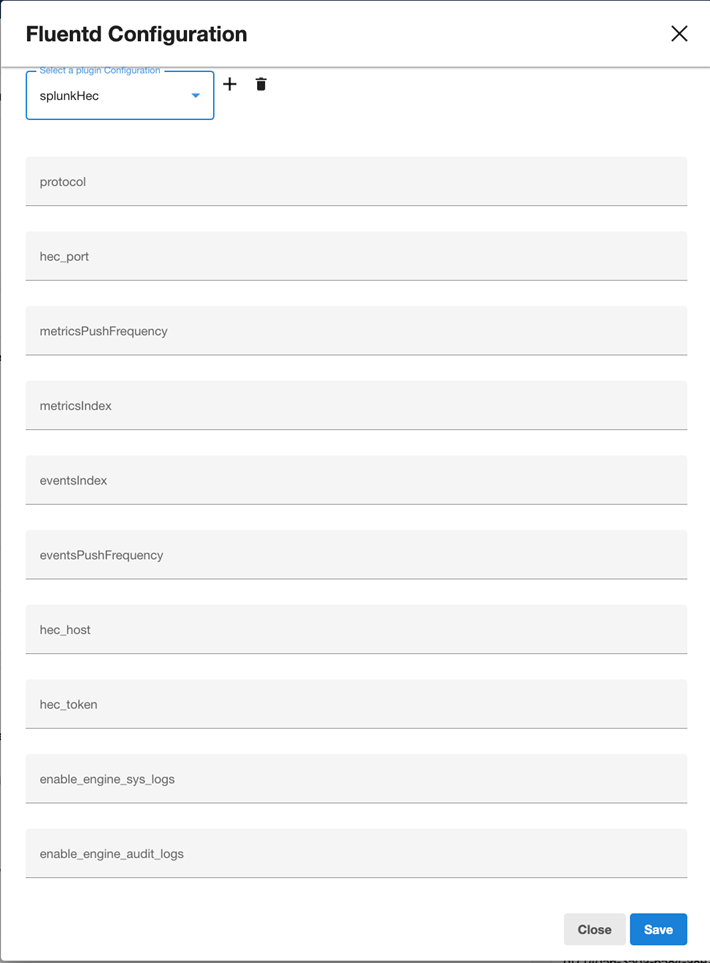
The splunkHec plugin appears in the drop-down by default.
-
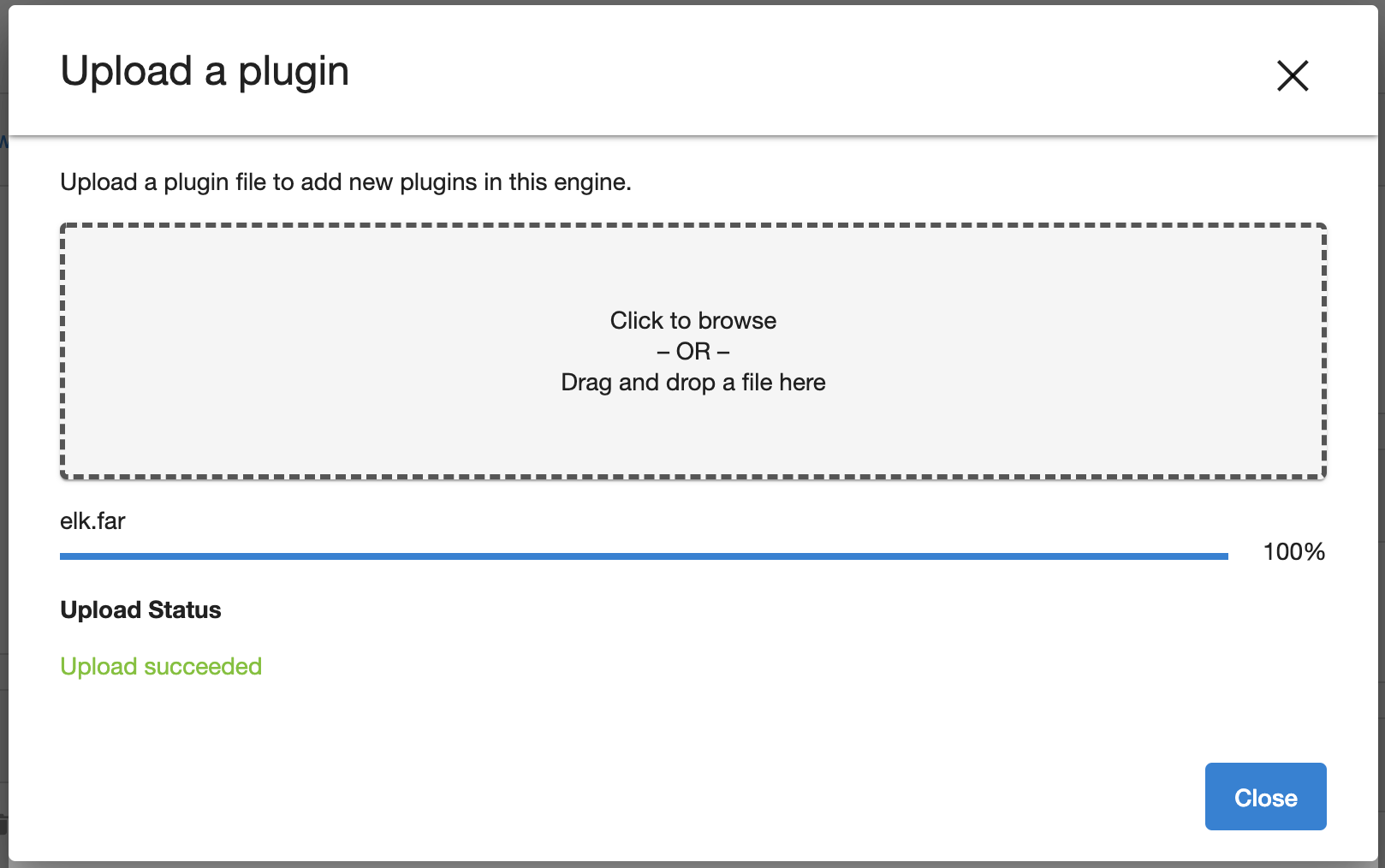
To add additional plugins, click the + button on the right.
-
You can view your new plugin in the drop-down menu. Select it to add a configuration.
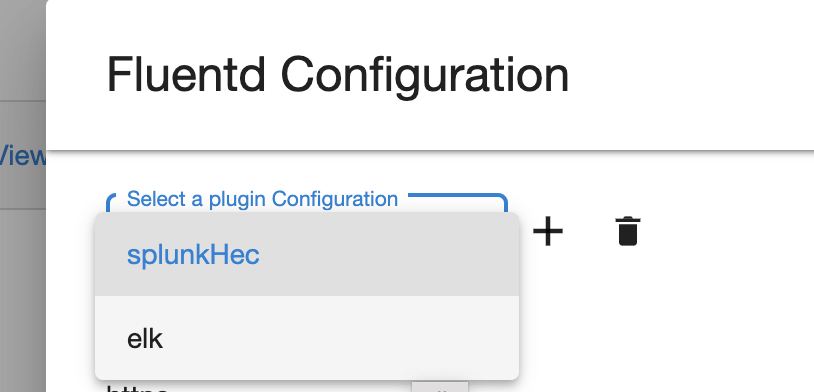
-
To delete your selected plugin, click the delete button on the right.
-
The name of fields to configure match those provided in the uploaded plugin file.
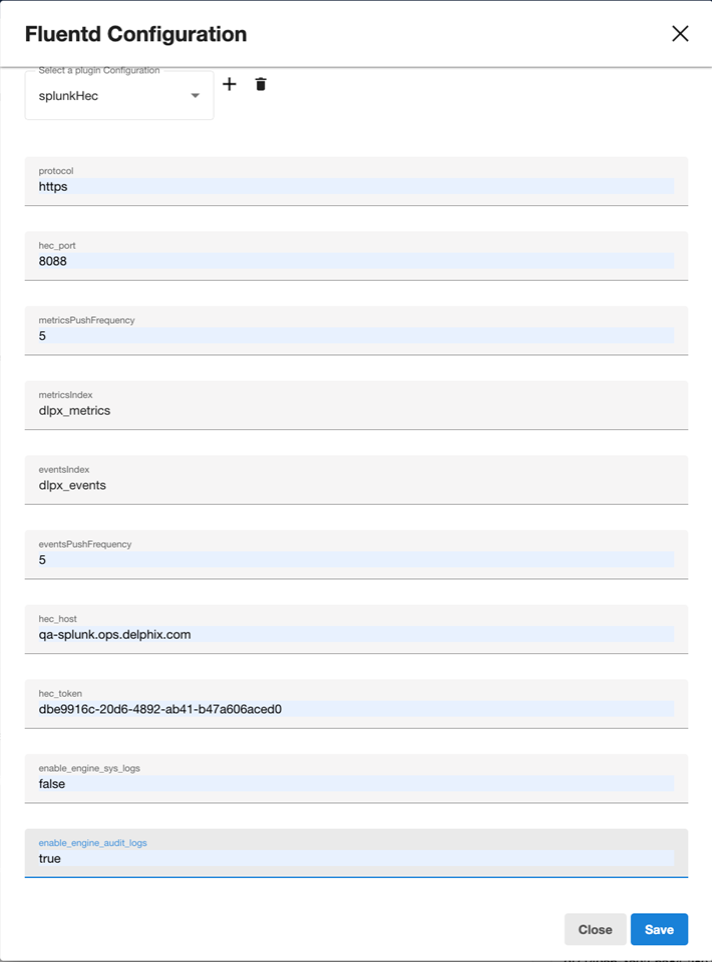
-
To save your configuration, click Save.
Troubleshooting
Occasionally, the Fluentd service might fail to start or encounter problems when sending logs to the remote data consumer. Typically, this is due to syntax errors in the plugin config file or network configuration problems on the data consumer server. These issues are generally reflected by error output in the fluent.log file, which you can access for download via the /service/fluentd/plugins/downloadFluentdLog API endpoint. Here is an example of downloading the log via curl:
curl -v -O -J "$delphix_engine/resources/json/delphix/service/fluentd/plugins/downloadFluentdLog" -b ~/cookies.txtImplementation
Secret attributes have been introduced to protect private data like passwords and tokens. In the CLI and API, you can identify them by the FluentdSecretAttribute type. In plugins, attribute names in the config file template beginning with _secret indicate secret data.
Known issues
Fluentd runs in a systemd container to limit negative side-effects from a bad plugin. You can add more security to this container by running as a non-root user, in addition to limiting the size of the log and buffer files it can write.